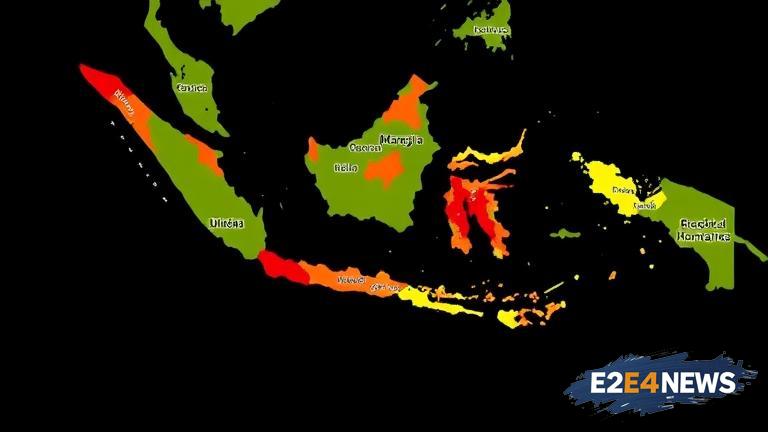
Indonesia, the world’s fourth most populous country, has been making significant strides in reducing poverty over the years. However, despite the progress, some provinces continue to struggle with high poverty rates. According to recent data, several provinces in Indonesia have poverty rates that are significantly higher than the national average. The provinces with the highest poverty rates are primarily located in the eastern part of the country. Papua, one of the most eastern provinces, has the highest poverty rate at 28.2%. This is followed by West Papua at 23.1%, and East Nusa Tenggara at 22.3%. Other provinces with high poverty rates include Maluku at 19.4%, North Maluku at 18.6%, and Gorontalo at 17.4%. The poverty rates in these provinces are attributed to various factors, including limited access to education and healthcare, lack of job opportunities, and inadequate infrastructure. The Indonesian government has been working to address these issues through various initiatives, including the implementation of social protection programs and investments in infrastructure development. Despite these efforts, the poverty rates in these provinces remain a concern. The high poverty rates in these provinces also have significant implications for the overall development of the country. Poverty can lead to a range of social and economic problems, including poor health outcomes, low levels of education, and limited economic opportunities. To address these issues, it is essential to implement targeted interventions that address the specific needs of each province. This includes investing in education and healthcare, creating job opportunities, and improving infrastructure. The Indonesian government has also been working to promote economic growth and development in these provinces through various initiatives, including the development of special economic zones and the promotion of tourism. However, more needs to be done to address the root causes of poverty and to ensure that all Indonesians have access to the opportunities and resources they need to thrive. The international community also has a role to play in supporting Indonesia’s efforts to reduce poverty. This includes providing financial and technical assistance to support the implementation of social protection programs and infrastructure development projects. By working together, it is possible to make significant progress in reducing poverty and improving the lives of millions of Indonesians. The data on poverty rates in Indonesia’s provinces is based on a recent survey conducted by the country’s statistics agency. The survey found that the poverty rate in Indonesia has declined significantly over the past few years, from 13.7% in 2018 to 12.3% in 2020. However, despite this progress, the poverty rates in some provinces remain a concern. The survey also found that the poverty rates are highest among certain groups, including farmers and fishermen. These groups often lack access to education and healthcare, and have limited job opportunities. To address these issues, the Indonesian government has been working to implement targeted interventions, including the provision of training and education programs, and the creation of job opportunities. The government has also been working to improve access to healthcare and education, particularly in rural areas. By addressing the root causes of poverty, it is possible to make significant progress in reducing poverty and improving the lives of millions of Indonesians. The issue of poverty in Indonesia is complex and multifaceted, and requires a comprehensive and sustained response. The government, international community, and civil society must work together to address the root causes of poverty and to ensure that all Indonesians have access to the opportunities and resources they need to thrive.